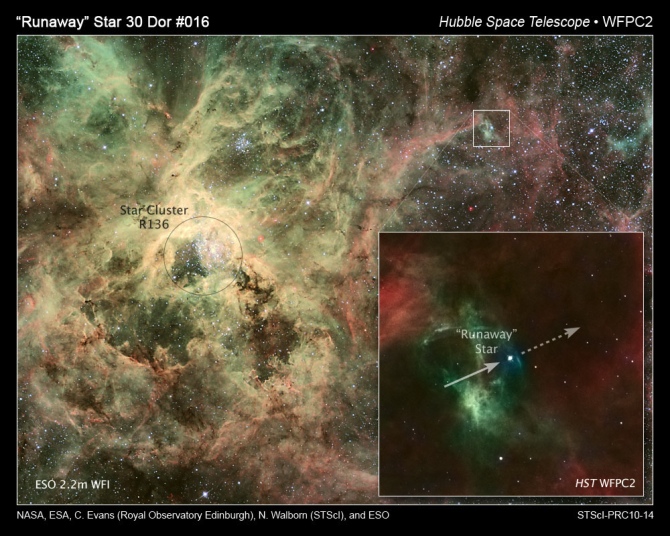
A runaway star strikes sooner and in a novel route
The picture voltaic and your total Milky Methodology’s stars are shifting in orbit all through the middle of our galaxy. The truth is, it’s kind of orderly, nonetheless there are native actions inside this major stream of stars, too. Astronomers have acknowledged some Milky Methodology stars which is maybe shifting sooner than anticipated, or in a route that appears uncommon. In view of this uncommon movement, they use the time interval runaway star to elucidate these renegades.
Stars type in clouds of gasoline and filth. Plenty of stars type from a single cloud. On account of this actuality, many Milky Methodology stars change by way of area in unfastened associations, or extra tightly certain open star clusters. By monitoring the motions of a runaway star, astronomers can often resolve its real stellar affiliation. Nonetheless, one issue must have occurred to kick the star into quick movement, on a path by way of area utterly completely totally different from its real cluster or affiliation.
The 2025 EarthSky Lunar Calendar makes an superior reward. Get yours immediately!
Astronomers diploma to 2 attainable causes for a runaway star
The primary state of affairs entails two binary star strategies – two strategies, every containing two stars – that go shut to no less than one one different. The encounter can disrupt each strategies and eject numerous stars at comparatively excessive speeds.
The second thought entails a supernova explosion in a numerous star system. These extraordinarily environment friendly explosions can propel related stars that didn’t explode alongside new paths, at much-higher speeds.
GD 50 may be from the Pleiades
One runaway star is GD 50, a white dwarf star with a bit extra mass than our picture voltaic, nonetheless smaller than the Earth. A dime as dense as GD 50 would weigh 2,600 kilos (~1,200 kilos) on Earth. GD 50 is all through the route of the constellation Eridanus the River. However, spherical 2009, astronomers who’d been finding out this star discovered that it strikes by way of area inside the same route and on the same tempo on account of the Pleiades star cluster.
And the Pleiades merely just isn’t far from Eridanus on the sky’s dome. GD 50 may be regarding the same age as stars all through the Pleiades. On account of this actuality, astronomers concluded that GD 50 was born all through the Pleiades, then flung out, presumably after passing too shut to a singular star.
One different runaway stars
Additional examples of runaway stars are AE Driver, 53 Aries and The pigeons. The truth is, they’re all shifting away from one another at velocities of over 100 km/s (for comparability, our picture voltaic strikes by way of the Milky Methodology at solely about 20 km/s sooner than the native frequent). Tracing their motions backwards on the sky’s dome, astronomers can see that – about 2 million years beforehand – the paths of those stars intersected close to the Orion Nebula. There’s a good loop or bubble of gasoline – often called Barnard’s Loop – surrounding Orion’s three distinguished Belt stars. Barnard’s Loop may very well be the remnant of the supernova that launched these stars as runaway stars.
Uncover runaway stars on Wikipedia
Backside line: Runaway stars change in a single different means from the final stream of stars in our Milky Methodology galaxy. Most probably basically essentially the most compelling proof suggests they have been kicked out from their real star clusters by encounters between pairs of binary stars or by a supernova explosion.
